Andro Youakim, Ehab G Daoud
Cite
Youakim A, Daoud EG. The pressure-volume curve, how to set PEEP. J Mech Vent 2021; 2(1):45-47.
Metrics
909 Downloads
https://www.journalmechanicalventilation.com/the-pressure-volume-curve-how-to-set-peep/
Abstract
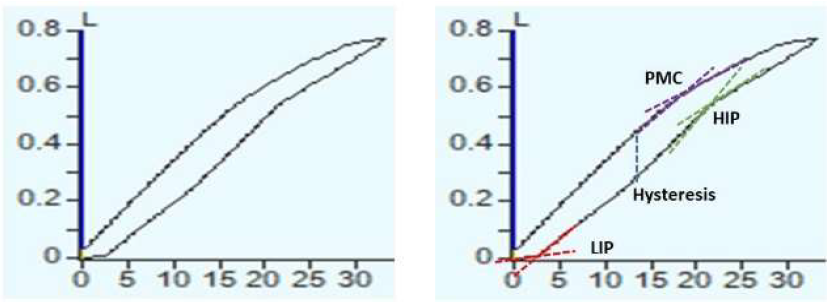
Figure 1: Pressure-Volume curve. Horizontal axis is airway pressure in cmH2O, vertical axis is resultant tidal volume in ml. LIP: Lower
inflection point, HIP: high or upper inflection point, PMC: point of maximum curvature or expiratory inflection point.
Keywords
Pressure-Volume curve, PEEP
References
| 1. Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, et al. Effect of a protective-ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 1998; 338(6):347-54. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199802053380602 PMid:9449727 |
| 2. Iotti GA, Braschi A. Measurements of respiratory mechanics during mechanical ventilation, Hamilton Medical Scientific Library, Rhazuns, Switzerland (1999) 66-82. Hamiltonmedical.nl. |
| 3. Lu Q, Vieira SR, Richecoeur J, et al. A simple automated method for measuring pressure-volume curves during mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 159(1):275-282. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.159.1.9802082 PMid:9872850 |
| 4. Arnal JM. Monitoring Mechanical Ventilation Using Ventilator Waveforms. 2018; Springer International Publishing AG. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58655-7 |
| 5. Chatburn RL (2003) Fundamentals of mechanical ventilation. Mandu Press Ltd, Cleveland Heights, OH. |
| 6. Gattinoni L, Carlesso E, Cressoni M. Selecting the “right” positive end-expiratory pressure level. Curr Opin Crit Care 2015; 21(1):50-57. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCC.0000000000000166 PMid:25546534 |
| 7. Maggiore SM, Jonson B, Richard JC, et al. Alveolar derecruitment at decremental positive end-expiratory pressure levels in acute lung injury: comparison with the lower inflection point, oxygenation, and compliance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med; 164:795-801. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.164.5.2006071 PMid:11549535 |
| 8. Takeuchi M, Goddon S, Dolhnikoff M, et al. Set positive end-expiratory pressure during protective ventilation affects lung injury. Anesthesiology 2002; 97:682-692. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200209000-00023 PMid:12218536 |
| 9. Albaiceta GM, Taboada F, Parra D, et al. Tomographic study of the inflection points of the pressure-volume curve in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004; 170(10):1066-1072. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200312-1644OC PMid:15317670 |
| 10. Demory D, Arnal JM, Wysocki M, et al. Recruitability of the lung estimated by the pressure volume curve hysteresis in ARDS patients. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34:2019-2025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1167-8 PMid:18575846 |
